Sheath blight is a common disease in rice fields, primarily caused by a fungus known as Rhizoctonia solani. This disease can occur from the time the rice seedlings are young until the panicles emerge. Infected rice plants will develop small, dark green spots on the leaves and leaf sheaths, which gradually turn into elliptical or cloud-shaped brown patches. In dry weather, these spots may turn yellow or gray in the center while the edges remain dark brown. In severe cases, the spots can merge into large areas, causing the rice leaves to yellow and even wither. If the stems and panicles are also infected, the rice may not grow well, fail to produce panicles, or have empty grains, significantly reducing the yield.
Sheath blight is most likely to occur in hot and humid conditions, especially when the temperature is between 18 and 34 degrees Celsius and the humidity is between 70% and 96%. If too much nitrogen fertilizer is applied in the rice field, or if it is applied too late, or if the plants are planted too densely, the disease can spread more easily. Therefore, controlling sheath blight is crucial for rice cultivation; otherwise, it can greatly affect the harvest.
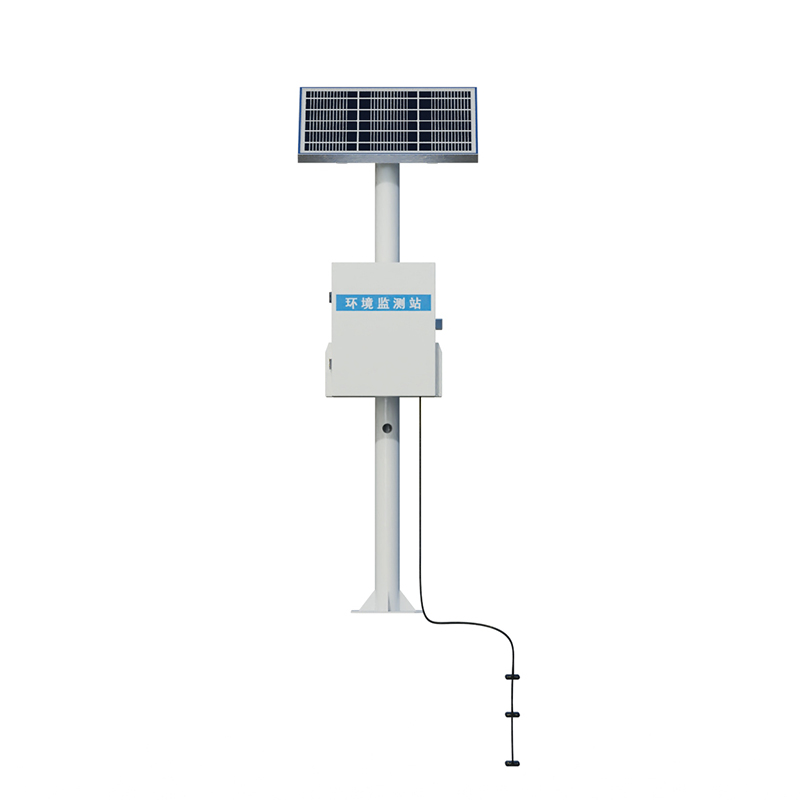
The Rice Sheath Blight Monitor FT-SD6 is a monitoring device that combines meteorological monitoring with intelligent spore capture and microscopic imaging technology. It can monitor the growth environment of the rice planting area in real-time, such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, and rainfall, and predict the occurrence of rice sheath blight through built-in models. The built-in spore capture device can collect the quantity and spread dynamics of sheath blight spores, providing an unmanned and visual monitoring method. Environmental meteorological information and images of sheath blight lesions are uploaded to a network platform in real-time, forming a dynamic comparative database that supports research on the relationship between the occurrence of sheath blight and meteorological conditions.

This paper addresses:https://fengtusz.com/industry/509.html